NASA’s Kepler Space Telescope has identified an Earth-like planet orbiting a nearby star within our galaxy’s habitable zone — often referred to as the “Goldilocks zone.”
This planet, known as Kepler-186f, is located about 500 light-years away in the Cygnus constellation.
The habitable zone, or Goldilocks zone, refers to the region around a star where conditions are just right — not too hot and not too cold — for a planet with sufficient atmospheric pressure to potentially maintain liquid water on its surface, a key ingredient for life as we know it.

While estimates suggest there are at least 40 billion Earth-sized planets orbiting stars in our Milky Way Galaxy, this particular discovery marks the first time an Earth-sized planet has been found within the habitable zone of another star.
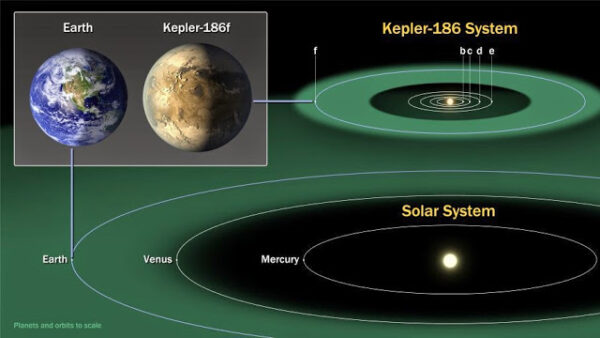
In addition to Kepler-186f, there are four other planets orbiting the same star within the Kepler-186 system. This raises exciting possibilities: if the host star shares characteristics with our own Sun, the chances of Kepler-186f supporting life increase significantly.
“We know of only one planet that hosts life — Earth,” said Elisa Quintana, research scientist at the SETI Institute at NASA’s Ames Research Center in Moffett Field, California, and lead author of the study published in Science.
“When searching for life beyond our solar system, we focus on finding planets with Earth-like qualities. Discovering a planet in the habitable zone that is also similar in size to Earth is a major milestone.”
The star that Kepler-186f orbits is about half the size and mass of our Sun, and it emits roughly one-third of the solar energy Earth receives. Kepler-186f completes an orbit around this star once every 130 days.









